This case study analyses the recent trademark infringement judgement delivered by a single judge bench of the Delhi High Court in the case of Burger King Co. LLC v. Virendra Kumar Gupta. (2023 SCC Online Del 2292, Burger King Co. LLC v. Virendra Kumar Gupta)
Trademarks are considered to be a highly valuable intellectual asset for businesses worldwide, often surpassing the worth of tangible assets. A trademark encompasses than.
just a name; it embodies a business& goodwill, reputation, and customer base. Therefore, it is crucial for businesses to monitor potential infringers in the market who may attempt to gain an unfair advantage by deceiving the public through the unauthorised use of a trademark belonging to an established and reputable brand. A comparable incident occurred with the well-known multinational fast-food chain, Burger King, when they discovered that a family-owned restaurant was operating under the name
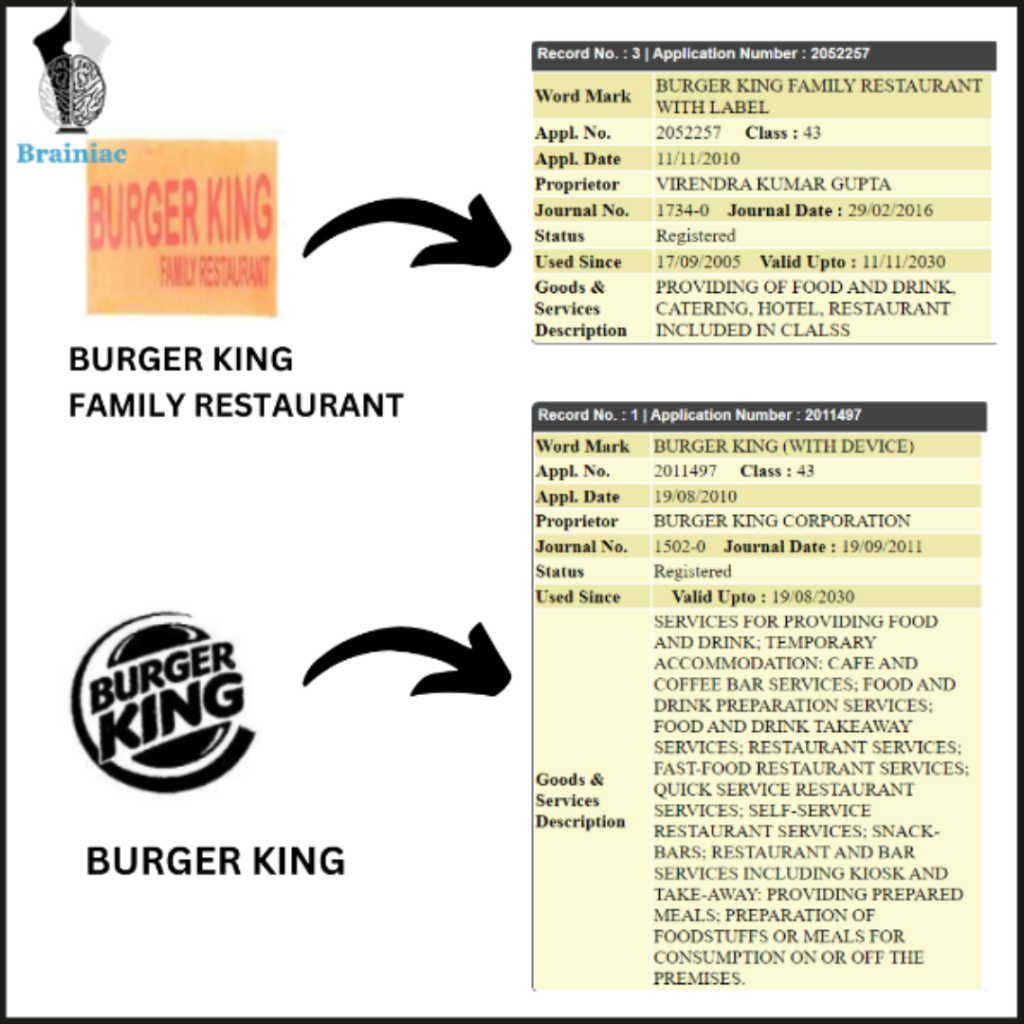
"Burger King." Furthermore, the same trademark had been registered in India since 2010.
Burger King originated in the United States in 1954 as a chain of burger restaurants. Since
then, it has expanded its business worldwide. Burger King currently operates in over 100
countries and has an estimated of 18,000 stores worldwide. Burger King made its debut in India in 2014 and later registered its trademark in 2017. Furthermore, Burger King is a widely recognised brand with over 200 stores located throughout India. In 2021, Burger King became aware of a family-owned restaurant operated by Virendra Gupta that uses the trademark 'Burger King& which has been in use since 2010. Burger King filed a rectification petition in the High Court of Delhi seeking for the cancellation of the
infringing mark on the grounds that it has been confusing the public and also tarnishing the reputation of a well-known mark. The company contended that the Trademark was registered with fraudulent intent and with the aim of benefiting from the Burger King company& reputation.
After hearing arguments from both sides, the High Court came to its decision that Virendra Kumar Gupta& registration of the "Burger King" trademark was, at the very least, fraudulent. The court made the observation that the family restaurant was not utilising the trademark in good faith and had adopted the mark with the goal of misleading customers.
In India, it is commonly seen that businesses do not normally strive to look for new and
unique names for their enterprises, but rather, they always aim to come up with names
sounding or looking similar to previously established major brands. This is because they
believe that this will attract more customers to their products or services. This ruling takes
a new level of significance in this regard, and it will most certainly be instructive for those who are operating their enterprises on the basis of copied trademarks. The decision also brought to light the significance of registering a person's trademark and making greater steps to protect it from unauthorised use or infringement.
#trademarkinfringement #trademark #whopperbattle #burgerkingtrademark
#burgerkinginfrinement