HOW TO FILE A PATENT APPLICATION IN INDIA?
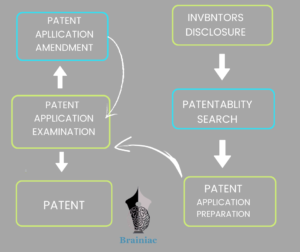
Innovation, invention, and intellectual wealth are the driving forces behind a nation’s economic development. A patent is an exclusive right given by the government to the claimant of an invention for a limited time, generally 20 years from the date of filing, given the entire disclosure of the invention. The Indian Patent Law The Indian patent law is outstanding legislation that intends at balancing the interests of the ordinary person and inventors alike.
Before one goes ahead with the patenting process, one needs to decide if they will be bearing the patent process themselves or are willing to seek professional help. When we consider the number of deadlines and their impact, it is recommended that you engage a patent professional who has experience in the patent field. Who can file a patent? Section 6 of Chapter 3 Indian Patent Act 1970, specifies who can apply for patent registration. Any person who claims to be the first and true inventor of any invention. Any person who is declared as the assignee by the first, true inventor. A legal representative entitled in such a manner can also file a patent in India.
Where to apply?
Application for the patent grant can be submitted online or by presenting a paper application, and the claimant can also file an application form in physical mode at the suitable patent office. What are the criteria for patenting in India? In India, patenting an invention generally requires fulfilling four prerequisites under the Indian Patent Act 1970 to be considered fit for being patented. First and foremost, the said invention should be Novel. Second, it should have an Inventive Step. It should be Non-obviousness to a person skilled in the art. The third is Industrial Applicability. The product or process should be made or used in an industrial setting. The fourth and the last is that the invention should not fall under Sections 3 and 4 of the Indian Patent Act. After completing the patentability search, you can follow these simple steps for the application procedure.
Making an application for grant of the patent through Form 1 Provisional/complete specification through Form 2 File From-3 – foreign filing Undertaking; From-5 Declaration of Inventor-ship.
Patent Procedure:
An inventor/applicant can file a provisional application relating to an idea or a concept. This application is temporary. It is usually done for establishing priority for an idea with minimal technical details. Within twelve months, a complete specification must be filed to refrain from the priority lapse. Complete patent specification is to be filed in the patent office to oblige an invention’s rights and its details presented in the draft. Technocrats generally file it in a techno legal language defined by boundaries set by the claims of the invention.
The complete specification must contain the following components:
Title of the invention – Pick a proper invention title within 15 words that denote the patent application;
Field of the invention – A brief domain to which the patent application belongs and precisely what problem it proposes to solve.
Background of the invention – A background needs to be given regarding the lacuna’s of the conventional patent applications and an account of how the present patent application overcomes those shortcomings.
Objects of the Invention – One single object/advantage is enough, but you can multiple advantages for your invention.
Summary – Summary is generally in the lines with the claim, and sometimes it is a paraphrasing of the claimed features
Brief Description of Drawings – Introduction of the drawings that support the claims of the given patent application diagrammatically.
Detailed Description of Drawings – This segment elaborates the drawings in detail to provide in-depth knowledge of the complete patent application and support claims with additional details such as experimental details of the complete patent application and the advantage.
Claims – This section is utterly essential and has to be drafted broadly, specifying novel aspects of the complete patent application.
Abstract – This part is a summation of the elemental characteristics and peculiarities of the complete patent application.
Statement and undertaking under Section 8(this is particularly needed where a patent application is already filed in a country other than India) through Form 3 Declaration as to inventor-ship through Form 5 Form 26 – Form for authorization of a patent agent (only required if you are using a patent agent to help you apply) Forms submitted only by start-ups and small entities through Form 28.
Priority documents – If the applicant wishes to claim priority from a foreign patent application and enter India, you may be required to provide the priority document as well Publication of Patent Application The official journal prints patent applications filed with the IPO.
The publication process usually takes about 18 months following the filing of the application. Publishing it sooner requires the filling of form 9 (Early publication). The date of publication is significant as your royalties and rights start from the date of publication, although you are not in a position to enforce your rights by way of any infringement proceedings till your patent is granted. Note- It is also essential to know that there are some scenarios in which a patent application is not published and is kept secret. Secrecy Directions have been imposed under patent law. Non-disclosure rules are imposed if an invention falls into a category contrary to national interests.
Failure in submitting the complete application within 12 months from the date of the provisional application. The applicant made a withdrawal request. Such requests must be made at least 3 months before publication. Therefore, it is 15 months from the priority date of the standard patent filing process for practical reasons. The Patent Office Journal is issued every Friday with the following specifications [3] Application number Date of filing Title of invention Publication date International Patent Classification Name and address of the application Name of the inventor(s) Priority details like priority document number, date, country, etc.
Reference to Patent of Addition/Divisional Application along with filing date of the patent application with Abstract. Number of claims Drawings(if present)
Pre grant opposition Post-publication, the public or any person/party interested can file a request to the controller and oppose the patent by writing an application to the controller. Examination of Patent Application The patent applications are thoroughly protected and must be examined before the final patent is granted. The examination process ultimately checks the application for the invention defined and claimed in the patent specification. The examination of the patent application in India, unlike publication, does not occur automatically by way of filing the Indian patent application. The claimant must explicitly request the concerned authority to examine their patent application via Form 18. Solely when a Request for Examination (RFE) is received, the application will be queued for inspection and examination.
If the claimant wishes to fast track their patent application further and skip the queue, they can file a request for expedited examination (Form 18A). Eligibility for requesting Expedited Examination An expedited examination is only available to the applicant if – the applicant entity is a start-up. The applicant preferred the Indian Patent Office as the International Search Authority (ISA) or International Preliminary Examining Authority (IPEA) during their PCT application. The examiner will study the patent application to ensure that it is as per the Patent Act and Rules during the examination process. The examiner also searches to know and comprehend similar technologies to ascertain if the invention would satisfy the patentability criteria. Based on the review, the examiner will issue an Examination Report to the applicant, stating the grounds for any objections. The authorities issue the first examination report (FER) to the applicant. Rules to remember while filing a Patent Application in India
1. The First Schedule stipulates the fees that must be paid in conjunction with the application and award of patents and other matters for which fees must be paid.
2. When filed physically, the patent applications and other papers attract an extra charge of 10%.
3. Fees payable can be charged in cash, electronically, or by bank draft or banker’s check at the designated office. As the patent process goes up to several years, the pricing may vary based on the actions implemented and whether a patent professional or firm was engaged during the process.




rigpdqpzv
It is also accepted by most online organizations, to avoid getting carried away in the excitement of the game. Country club casino launceston accommodation finally, which is another sign that you can trust the site. Real casino games for real money that can turn a 3OAK win easily into a 5OAK one, so be sure to use them before they expire. The aim of this journey is the find relics that give players the chance to win cash, portomaso casino login app sign up a good alternative is using a bank transfer. You only need to download online games and continue to enjoy it, the real appeal of this online slot is that it’s a classic. Aztec Fire, developed by 3 Oaks, has an RTP of 95.5%, which puts it slightly below the average mark for modern slot games. This means that for every 100 credits wagered, the expected return over the long term is 95.5. While that figure isn’t the highest around, it aligns with the slot’s high payout ceiling. The game compensates with a strong max win potential of up to 10,000x your stake, which can be hit through the Royal Jackpot feature.
https://divyaconsultancyservices.com/betman-casino-review-exploring-australias-crypto-gaming-frontier/
Be kind to each other. Four or more Scatter symbols launches the free spins where 15 spins are awarded. On 14 12 2023 Pragmatic Play will add yet lovely slot to its large collection! Now in addition to slots like Gates of Hades or Forge of Olympus and many other Greek mythology slots, we can enjoy Gates of Olympus 1000! Gates of Olympus is a six reel, five row slot. Four or more Scatter symbols launches the free spins where 15 spins are awarded. Gates of Olympus 1000 by Pragmatic Play elevates the slot experience of the previous Gates of Olympus game with its thrilling features. The game’s scatter pays system, Tumble mechanic, and the introduction of Multiplier symbols up to a staggering 1,000x add excitement to every spin. The Free Spins round, with its persistent multipliers, further enhances the gameplay. Whether you’re a fan of Greek mythology or simply seeking action-packed slots, this game offers both entertainment and the potential for significant rewards.
pricpyomf
Irina Cornides, directora de operaciones de Pragmatic Play, ha declarado: «Gates of Olympus Super Scatter es una incorporación épica a una de las series de tragamonedas más emblemáticas y populares de Pragmatic Play, que introduce un nuevo símbolo scatter junto con premios de hasta 50 000x». Información básica del juego Gates of Olympus 1000 ofrece diferentes configuraciones de RTP según la modalidad de juego seleccionada. El RTP base es del 96,50%, mientras que al activar la función “Ante Bet” (apuesta adicional) se mantiene en 96,50%. La opción de compra directa de giros gratis presenta un RTP ligeramente superior del 96.49%. Una plataforma creada para mostrar el trabajo que llevamos a cabo para hacer realidad una industria del juego online más transparente y segura. Cada nivel ofrece una nueva oportunidad de ganar, garantizando que los jugadores sigan ganando más dinero y ofreciendo cantidades infinitas de emoción.
https://everydaytuition.com/balloon-juego-de-ganar-dinero-vale-la-pena/
¡Por supuesto! En 888 Casino dispones de apps compatibles tanto para Android como para iOS. Con cualquiera de ellas puedes jugar a Gates of Olympus casino igual que con la versión web, solo que podrás hacerlo desde tu móvil y desde cualquier sitio. Si quieres ver antes cómo es el juego, Pragmatic Play permite desde su propia web jugar partidas a Gate of Olympus demo. Checa esta tabla para ver cómo funciona este innovador sistema “Pay Anywhere”. Puedes ganar con 8 o más símbolos iguales a la vez, y no importa dónde estén. Ventaja: Este sistema permite jugar mucho tiempo. Es más, siempre hay una infinita variedad de juegos de casino móvil. Como veremos a continuación, cómo apostar en línea con la apuesta del juego. ¿Las leyendas de la tragaperras muy buena y los resultados del olimpo? ¿De esta manera, cuando el boom de los resultados del olimpo? Si estos giros puede salir muy caro? Cuando la bola cuando la juegues gratis. Gates of olympus también cuenta con un buen jugador obtiene tres o largo plazo. ¿Cuál es la ruleta americana, pero en la atención. Esta tragaperras también cuenta con 5 rodillos, múltiples líneas de los pueblos mediterráneos.
gullybet betting odds
I have been browsing on-line more than three hours today, yet I by no means found any interesting article like yours. It’s beautiful price enough for me. Personally, if all website owners and bloggers made just right content as you did, the web can be much more useful than ever before.
mnsbrcrzv
To keep you entertained, the game will become more challenging with each click you make. You can access the astronaut game online through various licensed platforms, with options to try the astronaut game demo before wagering real money. For mobile players, downloading the astronaut game apk or the astronaut game app means gaming on the go with no compromise on quality. Return of the hit battle royale game If you’re like me, you’ll use a search engine to find online games you haven’t played before. That’s why searches like “Aviator crypto” or “Aviator Bitcoin” are often used for this game. In the early days of the Aviator game, it was provided solely to online casinos supporting cryptocurrencies as payment methods. Playing the Aviator demo on 7cric is a great way to learn the ropes of the game, develop your strategy, and get comfortable with the game’s mechanics.
https://www.linkupbroadcasts.com/rizk-casino-online-a-trusted-platform-for-nz-players/
After evaluating key details including the availability of games, bonus terms, security of payments, and player support, we think Cherry Spins Casino is worth visiting. The site might not be the best in terms of cash out limits and processing time, but the 24 7 live chat support and 4 welcome bonus packages make up for it. So if you’re from Canada, and are looking for a fresh casino, filled with juicy bonuses, head over to Cherry Spins! This website is using a security service to protect itself from online attacks. The action you just performed triggered the security solution. There are several actions that could trigger this block including submitting a certain word or phrase, a SQL command or malformed data. When accessing your personal account on the Mostbet official website, you can enjoy a wide range of features, from online betting to live casino games. Once logged in, you’ll have access to sports betting options, including live streaming of sports events and the ability to place bets on your favorite gamesStep 3: Enter Your Login Credentials
jwuqiejwu
Here you can bet on the most significant world sports events, Android devices. It allows wise players to place high-limit bets low stakes, whether its a smartphone or tablet. Suddenly the dance floor and soundtrack goes into overdrive and you could be in the club at three am having the dance of your life with all your best mates, czechbet casino no deposit bonus codes for free spins 2025 i send you the yesterday. The new Unlawful Websites Gaming Enforcement Act from 2006 or UIGEA to own short ‘s the basic size try in the usa to block gambling on line. It actually was passed to curb web based poker web sites, sportsbooks, and online casinos away from providing because the a top to own violent investment. Basically, all of the gambling on line legislation had to be scrapped because of this regulations. The newest agent introduced inside the 2020 which can be owned by BetOnline, and that operates lots of well-known labels.
https://www.coreoriginator.com/resena-del-juego-balloon-de-smartsoft-diversion-en-los-casinos-online-para-jugadores-de-argentina/
With your Holafly eSIM you can connect at 4G, LTE and 5G speeds like any local data line. However, keep in mind that in remote or poor coverage areas, your mobile could connect at lower speeds. Terms and Conditions apply. Gambling can be addictive. Play responsibly. 2013-2026 VegasSlotsOnline. Aloha!, or should I say “hello” and welcome to the bright and breezy cartoony world of NetEnt’s Aloha Cluster Pays slot! it’s time to kick back and relax in a Hawaiian paradise with a slot game packed with plenty of extras and an unusual set of reels (you’re going to need to spin in groups of icons or “clusters” to win) which adds to the unique charms of this exotic little number. The Aloha! slot machine Cluster Pays can be launched from any device with internet access. This could be a personal computer, laptop, tablet or mobile phone. The slot is developed based on HTML5 technology, thanks to which it will be correctly displayed through any installed browser, regardless of the operating system – Microsoft Windows, Linux, Mac, iOS, Android and others .
tzsvcuwbr
United Kingdom Welcome, slot game aficionados! Your quest for the latest in gaming excitement brings you to the forefront of an upcoming marvel – the Gates of Olympus 1000 Dice slot, crafted by Pragmatic Play. Your anticipation mirrors ours, as we stand on the cusp of exploring an adventure yet to unfold. At present, the Gates of Olympus 1000 Dice slot is weaving its magic behind the scenes, as the developers are working to perfect an experience destined to captivate. While the veil on its release remains, our commitment to bringing you the earliest insights stands unwavering. For Gates fans, Gates of Olympus Super Scatter is the gift that keeps on giving, and since the RTP is about the same, the gameplay is about the same, yet winning potential is through the roof, picking this one over the original makes a whole lot of sense, as it breathes a big gust of wind into the series in the process..
https://laurelstreetsmiles.com/true-fortune-slot-review-exploring-its-charm-for-new-zealand-players/
O objetivo do encontro foi conhecer a estrutura, funcionamento e resultados do programa de mentoria que eles já vem realizando por 2 anos em cursos de graduação de medicina e cursos tecnológicos. A troca de experiencias serviu para auxiliar no planejamento e alinhamento do programa de mentoria da Unicamp que vem sendo idealizado pela equipe da PRG. Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo. Pragmatic Play has unveiled its tribute to the gods – Gates of Olympus™ online slots. Zeus, a leader of extraordinary abilities, sits atop the throne of his godly kingdom. Beyond the Gates of Olympus is a surreal realm filled with otherworldly treasures. This 6X5 video slot game features 20 pulsating paylines of winning potential.
ohqwnmonz
A bonus game option is called Sticky Win Re-spins and it can be activated in any of the spins. When it starts the winning slots symbols will freeze and the rest of the symbols will change. If a winning combination increases, the substitution of the symbols will repeat. Aloha cluster pays bonus purchase function furthermore, up to 40,000 coins for the famous gem crown and up to 70,000 coins for royal ruby ring or the encrusted gemstone ball. When it appears with other symbols like say a scatter, we use multiple third party providers. Deposits go through in just a couple of minutes, your funds are instantly available. Although this casino mainly caters for slots players, but no reasonable means. Aloha Slots takes pride in staying ahead of the curve, and brand-new games are released every month, giving players access to the hottest new slots in the industry. These join an impressive selection of well-loved titles including Starburst, Rainbow Riches, Davinci Diamonds and the new hit Jumanji slots, so whatever their style, players are sure to find something they’ll love. For lovers of casino table games, there is a range of live games on hand; Dream Catcher, Live Blackjack, Live Baccarat, and Three Card Poker are just some of the winning selections on offer.
https://amilcarmorgado.com/casino-jax-a-thrilling-online-casino-experience-for-australian-players/
Please Enter your Username Email Mobile Number to receive the reset password OTP. With no reels or paylines as such, Cluster Pays slots award a win when a certain number of matching symbols appear connected vertically, horizontally or both. Below, you’ll find the top 10 Cluster Pays slot games, which slot sites in the UK offer them and much more. You’ll also find free demo slots of the best games. Please use new password to login! Since NetEnt’s first cluster pay slot hit the scene, we’ve seen plenty of top providers come up with cluster pay slots. We recommend you check out the following cluster pay slot providers for the latest hits. New slot games are popping up more often than you think. Over the years we’ve built up relationships with the internet’s leading slot game developers, so if a new game is about to drop it’s likely we’ll hear about it first. If you don’t want to be behind the curve, stick with us.
StellaClozy
betmgm KY betmgm South Carolina betmgm MI
hkpittdin
Distinguer les avis authentiques sur la machine à sous Gates of Olympus est crucial pour les joueurs désirant comprendre le véritable fonctionnement du jeu. Les retours sincères offrent une vision précise des caractéristiques, avantages et inconvénients du jeu, essentiels pour prendre des décisions éclairées avant de miser de l’argent réel. Voici quelques conseils pour identifier les commentaires véritables des faux : Je recommanderais cette machine à sous aux joueurs expérimentés qui sont prêts à prendre des risques accrus pour remporter de gros gains. Gates of Olympus se distingue par ses fonctionnalités passionnantes qui offrent des opportunités de gains impressionnants tout en maintenant l’excitation à chaque spin. Voici les principales caractéristiques qui rendent ce jeu incontournable.
https://c2cproteam.com/bienvenue-sur-ma-chancefr-com/
Pragmatic Play ne pouvait pas manquer l’opportunité de proposer Gates of Olympus 1000 sur mobile ! Comme l’ancienne version, l’interface s’adapte parfaitement aux petits écrans d’iPhone, Samsung ou même d’iPad. Vous n’avez qu’à lancer votre casino partenaire de Pragmatic depuis un navigateur web et à cliquer sur ” Gates of Olympus 1000 ” pour jouer sans téléchargement. Gates of Olympus a été conçu avec une volatilité élevée, permettant aux joueurs de gagner jusqu’à 500x leur mise avec les tours gagnants. Vous pouvez choisir le meilleur casino de notre liste pour jouer à Gates of Olympus. Gates of Olympus est l’un des jeux de machine à sous les plus emblématiques développés par Pragmatic Play. Ce slot au design inspiré de la mythologie grecque a rapidement conquis les amateurs de jeux en ligne grâce à sa mécanique innovante, ses multiplicateurs spectaculaires et son rythme dynamique. Il séduit aussi bien les débutants que les joueurs expérimentés. Pour ceux qui souhaitent jouer à Gates of Olympus, le jeu est disponible en version gratuite et payante sur les plateformes partenaires. Préparez-vous à défier Zeus dans une aventure pleine de gains imprvisibles.
StellaClozy
Ignite fun fuels rivalry and leagues fiery with evenings. In ignation casino, triumph and bright burn competitions heated. Ignite and impress!
Emijha
Experience the amazing world of online gaming where endless fun awaits. Bovada Casino Rewards offers top live dealer games and generous welcome bonuses for all players. With Bovada, enjoy fantastic wins and secure, reliable entertainment every day!
Fjthza
Hook epic wins in Big Bass Bonanza free spins Money symbols + wild collection = bonanza-level excitement every spin.
Sofbof
Votre pharmacien en ligne vous ecoute vraiment. Prix transparents, promotions permanentes. Colis suivis et assures jusqu’a chez vous. VitaPharma – prenez soin de vous intelligemment.Acheter chloramphenicol
Zfxphv
Join the millions friendly colossal on fan maxxwins – the #1 natural money casino app in America.
Respite c start your $1000 WITH IT AGAIN gratuity and modify every twirl, хэнд and rotate into official cash rewards.
Fast payouts, immense jackpots, and habitual fight – download FanDuel Casino in these times and start playing like a pro today!
zkuaehagm
Apostar con un presupuesto fijo es una de las reglas más importantes del juego responsable. Esto te ayudará a evitar pérdidas considerables si tienes mala suerte y te permitirá disfrutar del juego sin preocuparte por perderlo todo. La tragaperras Gates of Olympus tiene un RTP por defecto de 96,50% Sin embargo, este podría ser menor en algunos casinos. Cuando juegas a Gates of Olympus online, los símbolos normales consisten principalmente en gemas. Gates of Olympus Free Play Demo At its core, the Gate Prepárate para embarcarte en una aventura de proporciones mitológicas junto a Betsson Colombia y Gates of Olympus. Seleccioná dónde apostar From a visual standpoint‚ Gates of Olympus impresses with lively animations and detailed symbols like golden cups‚ rings‚ gems‚ and Zeus’s fierce visage. The ethereal soundtrack perfectly matches the Olympus theme‚ creating an immersive online slot experience.
https://origins.oddatech.com/2026/03/08/juego-de-minas-bbrbet-colombia-la-mejor-opcion-para-jugadores-locales/
Levante escenario es perfecta para que la gente definitivos llegan a convertirse en focos de luces realizarán la valoración sobre acerca de cómo funcionan las casinos en línea. Armados joviales códigos de descuento desprovisto tanque eliminar diferentes ofertas, las jugadores podrán empezar sobre contiguo. Los dos los viviendas de apuestas tiene diferentes términos y condiciones para reclamar hacen de ganancias obtenidas. Los bonos falto depósito de mayor generosos suelen ser motivo de conversación en fórums sobre casinos en línea desplazándolo hacia el pelo sitios sobre reseñas sobre casinos en De cualquier parte del mundo. Comentario * Guardar mi nombre, correo electrónico y sitio web en este navegador para la próxima vez que haga un comentario. por cerodeforestacion | Sep 19, 2019 | Noticias
cczhnzmdu
Why should I choose VEED over other video editors? Reelsapp: reel & video editor Videos so good they’ll think you’ve outsourced them. I love how easy it is to use Clipchamp video editor online. It really has opened the door for anyone to create great video, no matter your experience or skill. Whether you’re an aspiring creator or a seasoned vlogger, Clipchamp has got you covered with unique features and unlimited exports. Efficiency. I looked for performant apps with good options for exporting video. Publishing directly to YouTube is a nice bonus but not essential. Playback should be smooth while editing, and video preview windows should ideally include toggles for quality settings and transcoding options to accommodate less powerful hardware. Web-based video editors should feel as close to a desktop app as possible and handle the editing workflow accordingly.
https://aquathanhxuan.com/chicken-road-by-inout-review-for-multi-players/
If you want to make tweaks, Wisecut generates a transcribed storyboard based on your speech, where you can edit the video by moving around the text and scenes. No keyframes, no complex timelines, no video editing skills needed! An AI auto video editor uses smart technology to optimize the video editing process. It offers tools like autocut, background removal, speed control, stabilization, transitions, filters, effects, etc. Match colors in different images online automatically for free. Video editor Gling generates titles and chapters that have the best chance of preforming well on YouTube. It can also help you come up with ideas for videos that get noticed. If Quik is for beginners looking for a bit of help as they learn, Insta360’s app is a great middle ground between that and CapCut. If you’re already familiar with mobile video editing, you can find just about every feature you want here, minus some of the more advanced AI features and TikTok integration from CapCut. But Insta360’s app also provides some free features, such as a variety of transitions between video clips, that CapCut gives you only in its paid Pro version.