Executive Summary
One of the fundamental requirement in today’s world is transport. Petrol and diesel engines fulfil the requirement but with the cost of pollution and other hazards. Now the traditional combustion engines are becoming outdated with the replacement of fully electric vehicles. Fully electric vehicles (EVs) have zero emission which is better for the environment. There are several advantages with the use of EV. The very first is the lower running cost. This is because charging of the electric vehicle is cheaper than the petrol/diesel prices. Also, the maintenance cost for such vehicles is less. The government is also providing tax and financial benefits by giving incentives.
Introduction
An EV is defined as a vehicle that can be powered by an electric motor that draws electricity from a battery and is capable of being charged from an external source. An EV includes both a vehicle that can only be powered by an electric motor that draws electricity from a battery (all-electric vehicle) and a vehicle that can be powered by an electric motor that draws electricity from a battery and by an internal combustion engine (plug-in hybrid electric vehicle).
Electric vehicles have low running costs as they have fewer moving parts for maintenance and are very environmentally friendly as they use little or no fossil fuels (petrol or diesel). While some EVs used lead acid or nickel metal hydride batteries, the standard for modern battery electric vehicles is now considered to be lithium-ion batteries as they have a greater longevity and are excellent at retaining energy, with a self-discharge rate of just 5% per month. Despite this improved efficiency, there are still challenges with these batteries as they can experience thermal runaway, which have, for example, caused fires or explosions in the Tesla model S, although efforts have been made to improve the safety of these batteries.
History of Electric Vehicles
- Anyos Jedlik built the first crude but viable electric motor, which used a stator, rotor, and commutator in 1827; and the next year he used it to power a small car.
- The first known electric locomotive was built in 1837, in Scotland by chemist Robert Davidson of Aberdeen. It was powered by galvanic cells (batteries).
- A patent for the use of rails as conductors of electric current was granted in England in 1840, and similar patents were issued to Lilley and Colten in the United States in 1847.
- The first battery rail car was used in 1887 on the Royal Bavarian State Railways.
- In 1959, American Motors Corporation (AMC) and Sonotone Corporation announced a joint research effort to consider producing an electric car powered by a “self-charging” battery.
- At the 1990 Los Angeles Auto Show, General Motors President Roger Smith unveiled the GM Impact electric concept car, along with the announcement that GM would build electric cars for sale to the public.
- The passage of the Electric and Hybrid Vehicle Research, Development and Demonstration Act of 1976 in the US provided government incentives for development of electric vehicles in the US.
- California electric car maker Tesla Motors began development in 2004 on the Tesla Roadster, which was first delivered to customers in 2008.
- The Roadster was the first highway legal serial production all-electric car to use lithium-ion battery cells, and the first production all-electric car to travel more than 320 km (200 miles) per charge.
- The Nissan Leaf, introduced in Japan and the United States in December 2010, became the first modern all-electric, zero tailpipe emission five door family h
- In March 2020 the Tesla Model 3 passed the Nissan Leaf to become the world’s all-time best-selling electric car, with more than 500,000 units delivered.
Taxonomy
The technology taxonomy focuses on classifying patents based on the technological aspects and innovations within and around EVs. The categorization of patents and patent applications around EVs was done based on technical/functional components and their application areas. It mainly types of batteries used in India and their manufacturers.
The set considered for the analysis comprises of 2033 live patents/patent applications out of 2303
Types of energy storage used in India:
- Lithium-ion batteries
- Lead-acid batteries
- Nickel-Metal Hydride batteries
- Ultracapacitors
Manufacturers of batteries in India
- Exide Industries
Exide is very popular in the battery manufacturing market. It has collaborated with many developers to produce cost-effective and durable lithium-ion batteries for electric vehicles.
- Maruti Suzuki
The company has collaborated with Toshiba and Denso for manufacturing electric vehicles and energy storage batteries.
- Tata Group
The company has partnered with Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO) to develop lithium-ion battery producing plants throughout the nation.
- Hero Motors
The Hero MotoCorp has built a new facility in Tamil Nadu for the manufacturing of EVs and has done strategic investments in the lithium-ion batteries manufacturing.
- Amara Raja Batteries
The Amaron is the famous battery manufacturer in India. Like Tata Group, Amara Raja has collaborated with ISRO to produce lithium-ion batteries for EVs.
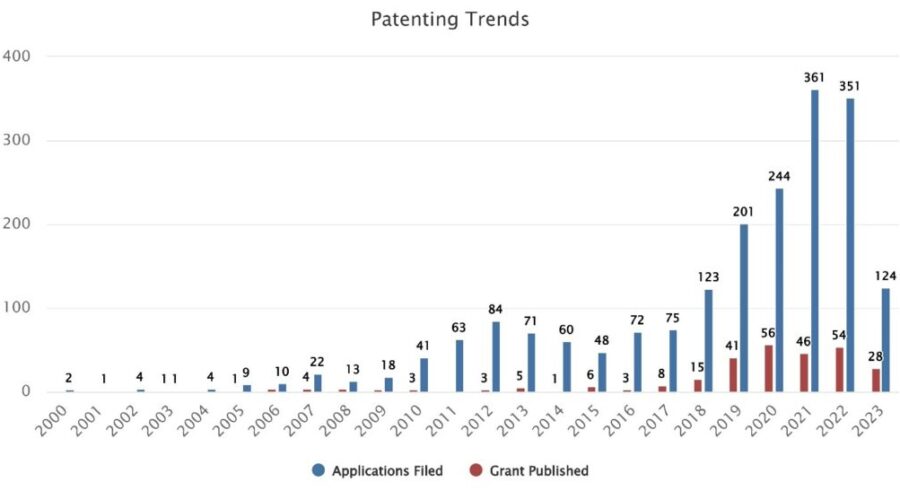
Patenting Trend.
There has been gradual increase since 2010 in patent filling for the inventions related to EVs. In 2020, the highest number of grants were published.
Upcoming companies filing patents in India.
- AULTON NEW ENERGY AUTOMOTIVE TECH CO LTD
- SHANGHAI DIANBA NEW ENERGY TECHNOLOGY CO LTD
- OLA ELECTRIC MOBILITY PVT LTD
- KWANG YANG MOTOR CO LTD
IPLTECH ELECTRIC PVT LTD.